Yamaha YZF-R125 Service Manual: Outline of the fi system
The main function of a fuel supply system is to provide fuel to the combustion chamber at the optimum air-fuel ratio in accordance with the engine operating conditions and the atmospheric temperature. In the conventional carburetor system, the air-fuel ratio of the mixture that is supplied to the combustion chamber is created by the volume of the intake air and the fuel that is metered by the jet used in the respective carburetor.
Despite the same volume of intake air, the fuel volume requirement varies by the engine operating conditions, such as acceleration, deceleration, or operating under a heavy load. Carburetors that meter the fuel through the use of jets have been provided with various auxiliary devices, so that an optimum airfuel ratio can be achieved to accommodate the constant changes in the operating conditions of the engine.
As the requirements for the engine to deliver more performance and cleaner exhaust gases increase, it becomes necessary to control the air-fuel ratio in a more precise and finely tuned manner. To accommodate this need, this model has adopted an electronically controlled fuel injection (FI) system, in place of the conventional carburetor system. This system can achieve an optimum air-fuel ratio required by the engine at all times by using a microprocessor that regulates the fuel injection volume according to the engine operating conditions detected by various sensors.
The adoption of the FI system has resulted in a highly precise fuel supply, improved engine response, better fuel economy, and reduced exhaust emissions.
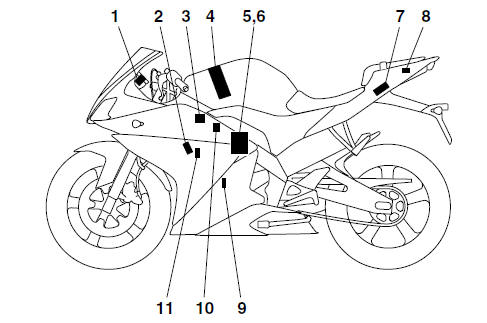
- Engine trouble warning light
- Spark plug
- Ignition coil
- Fuel pump
- FID (fast idle solenoid)
- Throttle body sensor assembly (consisting of throttle position sensor, intake air pressure sensor, intake air temperature sensor)
- ECU (engine control unit)
- Lean angle sensor
- Crankshaft position sensor
- Fuel injector
- Coolant temperature sensor
 Features
Features
...
 Fi system
Fi system
The fuel pump delivers fuel to the fuel injector via the fuel filter. The
pressure regulator maintains the
fuel pressure that is applied to the fuel injector at only 250 kPa (2.50 kg/cm²,
36 ...
Other materials:
Assembling the oil pump
1. Lubricate:
Oil pump inner rotor
Oil pump outer rotor
Oil pump driven gear
(with the recommended lubricant)
2. Install:
Oil pump outer rotor
Oil pump inner rotor "1"
Oil pump driven gear
Pin "2"
NOTE:
When installing the inner rotor, align the pin "2"
in the oil pump sh ...
Installing the front fork legs
The following procedure applies to both of the
front fork legs.
1. Install:
Front fork leg
Temporarily tighten the upper and lower
bracket pinch bolts.
NOTE:
Make sure the inner tube end position "a" is 24.5
mm (0.96 in) from the top of the upper bracket.
2. Tighten:
Lower br ...
Parking
When parking, stop the engine, and
then remove the key from the main
switch.
WARNING
Since the engine and exhaust
system can become very hot,
park in a place where pedestrians
or children are not likely to
touch them and be burned.
Do not park on a slope or on soft
ground, ...
